How to Monitor Compliance in Automated Workflows
Local Services
Dec 31, 2025
Dec 31, 2025
Ensure real-time compliance in automated workflows with standards, scanning tools, approval thresholds, audit trails, and KPIs to reduce risk.

Monitoring compliance in automated workflows is about ensuring your systems follow regulations, legal standards, and internal policies in real time. This approach prevents costly mistakes - like a single compliance issue that could cost up to $4 million - and protects your business from legal and financial risks.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
Define Compliance Standards: Identify industry-specific regulations (e.g., OSHA, FLSA) and assign clear roles for monitoring.
Use Automation Tools: Implement software to track actions, flag issues, and maintain audit trails.
Set Approval Workflows: Establish thresholds for human intervention in high-stakes decisions.
Track and Log Actions: Keep detailed records to ensure accountability and transparency.
Measure KPIs and Audit: Use metrics like error rates and task completion times to evaluate your system, and conduct regular audits.
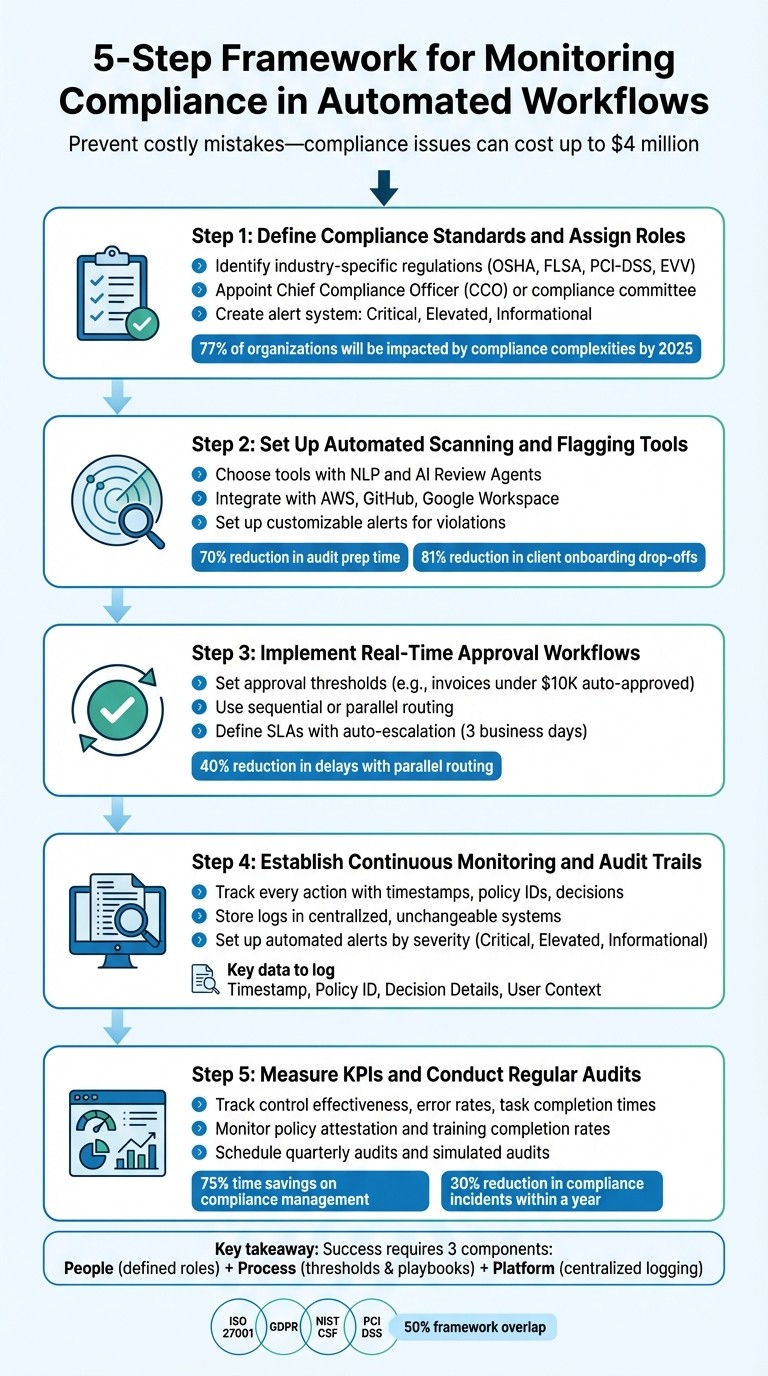
5-Step Framework for Monitoring Compliance in Automated Workflows
Step 1: Define Compliance Standards and Assign Roles
Identify Industry-Specific Compliance Standards
Before diving into automation, it’s crucial to outline all relevant regulations. Local service companies often navigate a complex, three-tiered compliance framework: federal laws, state-specific requirements, and industry guidelines. For example, what works in Texas might not align with California’s stricter rules, like mandated meal and break periods [9].
Start by reviewing guidelines from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), especially if your team handles fieldwork. HVAC technicians managing refrigerants, landscapers using heavy machinery, or janitorial staff working with industrial chemicals all need to follow OSHA safety protocols [9][13]. Next, ensure compliance with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) to guarantee that your automated systems accurately handle overtime and minimum wage calculations [9]. If your business involves federally funded construction projects, the Davis-Bacon Act requires certified payroll reports to document prevailing wages - automation can reduce errors in these reports by as much as 75% [9][11].
For businesses managing payments, adhering to PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is mandatory [10][12]. Similarly, home care agencies receiving Medicaid funding must comply with Electronic Visit Verification (EVV), which uses tools like location tracking and digital signatures to confirm service delivery [9]. Once you’ve identified the relevant standards, the next step is assigning roles to oversee compliance across automated workflows.
Assign Responsibilities for Compliance Monitoring
With the regulations clearly defined, it’s time to delegate responsibilities for maintaining compliance. Automation doesn’t mean you can set it and forget it - oversight is still necessary. Consider appointing a Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) or forming a compliance committee that reports directly to the CEO [2]. For smaller teams, assign specific roles to track technical metrics and verify the accuracy of data [3].
Create an alert system with clear action plans. For example, critical alerts should trigger immediate responses, elevated alerts require timely investigations, and informational alerts can guide ongoing improvements [3]. To maintain transparency, separate responsibilities - those monitoring compliance shouldn’t be the same people executing the automated tasks [2]. For industries like HVAC, landscaping, and janitorial services, designate someone to oversee adherence to OSHA safety rules and EPA standards, which regulate everything from chemical handling to emissions [13][15]. With compliance complexities projected to impact 77% of organizations by 2025, having clearly defined roles is more important than ever [14].
Step 2: Set Up Automated Scanning and Flagging Tools
Choose the Right Tools for Compliance Automation
Once you've defined your compliance standards and assigned responsibilities, it's time to choose tools that enable continuous monitoring and automated oversight. Unlike periodic or annual audits, these tools work around the clock, helping you catch issues before they turn into costly violations. Here’s why this matters: organizations lose an average of $4 million in revenue from a single non-compliance incident [5][2].
Look for tools equipped with natural language processing (NLP) to analyze complex regulatory texts and automatically update your internal policies [8]. AI Review Agents can also help by pre-checking evidence for completeness and formatting, saving time before human review [5]. If your business operates in industries like field services, make sure your tools integrate smoothly with platforms like AWS, GitHub, or Google Workspace. This way, you can automate the collection of access logs, certifications, and version histories without the need for manual input [6].
Take, for example, Diamond IT. In October 2025, its owner, Matt Mayo, integrated GitHub, Google Workspace, and AWS into their compliance system. This change turned their SOC 2 audit prep from an annual headache into a continuous process, cutting audit preparation time by 70% and allowing the team to spot and fix policy deviations in real time [6]. Similarly, a financial services firm implemented automated KYC document collection in 2025, reducing client onboarding drop-offs by 81%. They replaced manual email follow-ups with AI-driven workflows and validation processes [5].
These success stories highlight how the right tools can align with your compliance goals. Prioritize scanning tools that offer customizable alerts to notify stakeholders immediately about policy violations, misconfigurations, or suspicious activity [8]. Some tools even use machine learning to predict risks, helping you address potential issues before they escalate [8]. For industries like HVAC, landscaping, or janitorial services, automated remediation features - such as revoking unauthorized access or blocking non-compliant transactions - can stop violations from spiraling out of control [8].
Feature | Manual Workflow | Automated Workflow |
|---|---|---|
Evidence Collection | Screenshots and email follow-ups | Automated file requests with AI checks |
SLA Management | Spreadsheet tracking | Automated reminders and escalations |
Audit Readiness | Year-end scramble | Real-time audit trails |
Error Risk | High due to manual data handling | Low with direct system integrations |
Once you’ve selected the right tools, the next step is to integrate them into your current workflows for seamless compliance monitoring.
Integrate Compliance Tools into Your Existing Workflows
To ensure smooth adoption, start by automating high-volume, low-risk tasks, then gradually expand to more complex risk assessments [6]. This phased approach minimizes disruption and allows your team to build confidence in the system. Use API-first integrations with OAuth 2.0 to connect tools securely, and fine-tune alert criteria to avoid overwhelming your team with unnecessary notifications [17][16].
For businesses managing automated engagement workflows through platforms like Cohesive AI, proper integration ensures that customer interactions stay within compliance boundaries. For instance, when adding a new vendor or updating a policy, your tools can automatically trigger scans and set escalation rules for overdue tasks [4].
To involve external stakeholders, such as vendors or clients, without complicating their experience, consider using Magic Links. These secure, one-time links allow users to submit evidence or complete scans without needing to create new accounts [5]. In one example, an accounting firm automated its tax season document requests in 2025. This change reduced email clutter by 95% while maintaining an audit-ready trail for every client submission [5].
"Do the menial labor with a computer, and the computer labor with a human." – Mircea Dima, CTO and Software Engineer, AlgoCademy [6]
Automation is a powerful tool, but it should complement - not replace - human expertise. Adopt an Expert-in-the-Loop (EITL) model, where automated alerts are reviewed by specialists for final decisions [6]. This hybrid approach ensures that AI handles repetitive, data-heavy tasks while your team focuses on interpreting complex regulations. In fact, 75% of compliance leaders in 2023 identified this balance as critical for managing increasingly intricate programs [4].
Q-Compliance: Achieve Real-Time Compliance Automation
Step 3: Implement Real-Time Approval Workflows
After automating scanning processes, the next step is to establish real-time approval workflows for decisions that carry more weight.
Set Approval Thresholds for Automated Actions
Start by automating straightforward tasks and setting clear thresholds for when human intervention is required. For example, invoices under $10,000 can be processed automatically, while anything above that amount gets routed to a director or CFO for approval [18].
Assign approval responsibilities to specific roles, like a Compliance Manager or Regional Director, to ensure smooth operations even during staff changes [18]. Multi-stage routing can further streamline the process. Sequential routing requires one person to approve before the next reviewer steps in, while parallel routing lets multiple stakeholders review at the same time, cutting potential delays by as much as 40% [18].
AI can play a key role by pre-screening documents for completeness and compliance. It can provide an "Approve" or "Reject" recommendation, but the final decision remains in human hands [19]. This added layer of real-time approval ensures that only actions aligned with policies move forward.
To avoid bottlenecks, define service-level agreements (SLAs). For instance, approvals that remain pending for more than three business days can automatically escalate to higher authorities. Every approval action should be logged with details like timestamps, IDs, and comments [18] [1]. Exception management built into workflows can speed up resolutions by as much as 40%.
These thresholds create a foundation for selecting automation platforms that support advanced, multi-stage approval processes.
Use Workflow Automation Platforms with Built-In Approval Systems
Once you've set thresholds, choose a platform that can implement them effectively. Tools like Microsoft Power Automate provide built-in approvals with options like "Everyone must approve", "First to respond", and sequential routing. Its integration with Outlook and Microsoft Teams ensures approvers receive real-time notifications [20]. For companies using platforms like Cohesive AI to manage automated workflows, this integration keeps customer interactions and lead generation activities compliant while maintaining efficiency.
Microsoft Copilot Studio takes this a step further by combining AI screening with human oversight in multi-stage approvals [19]. Similarly, Moxo offers a drag-and-drop Flow Builder with AI Review Agents that can pre-validate documents like vendor certifications or access logs before they reach human reviewers [4]. In one case, a financial services firm used Moxo in October 2025 to automate vendor certifications, cutting audit preparation time from three weeks to just five days [4].
It's essential to test the approval system with edge cases, such as threshold values or missing data, to ensure rejection and escalation logic works as intended [19].
Workflow Component | Role in Compliance | Example Setup |
|---|---|---|
Trigger | Initiates the workflow | New vendor added; policy update published [4] |
Action | Executes an automated task | Sending file requests; routing for e-signature [4] |
Control | Maintains compliance | Escalating overdue requests; conditional branching [4] |
Threshold | Flags for human review | "If amount > $10,000, route to Director" [18] |
Step 4: Establish Continuous Monitoring and Audit Trails
After setting up approval workflows, the next step is to ensure every automated action is tracked and logged. This creates a clear audit trail and helps identify issues before they can lead to compliance failures.
Track and Log Every Automated Workflow Action
Detailed logs are the backbone of accountability. They record every automated decision with key details like timestamps, policy IDs, actions taken, resource information, and any violation messages [21]. These logs provide the necessary context for human intervention and decision-making, as emphasized in Step 3.
To safeguard these records, store them in centralized, unchangeable storage systems [3][5]. Use a unified JSON schema across all policy engines and platforms to simplify monitoring [21]. At a minimum, logs should include:
Timestamp: Example format - 12/31/2025 10:00:00 AM.
Policy ID: For instance, "access-control-v2."
Decision Details: The action taken and the associated resource.
User Context: Identifying who or what triggered the workflow.
Adding metadata such as application names and business units enhances the logs, making it easier to create actionable dashboards [21]. For example, if you're using tools like Cohesive AI for automated lead generation, these logs can document every email, contact interaction, or data scraping activity. This level of detail is particularly important when dealing with sensitive information from sources like Google Maps or government filings.
Set Up Automated Alerts for Anomalies
Once detailed logs are in place, use them to power real-time alerts that identify and address issues as they happen. Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) can detect vulnerabilities and deviations immediately, ensuring problems are caught early [4][5].
To avoid overwhelming your team, categorize alerts by severity:
Critical Alerts: Require immediate attention and should trigger notifications via tools like Slack or PagerDuty.
Elevated Alerts: Need investigation during normal business hours.
Informational Alerts: Help track long-term trends and improvements [3][21].
Group notifications by policy and resource ID, and limit reminders to set intervals (e.g., every 24 hours) for unresolved violations [21]. Escalations should be automated - if a compliance task, such as acknowledging a policy, isn't completed within a set timeframe (e.g., three business days), higher-level stakeholders should be notified [4].
Finally, don't forget to monitor the health of your monitoring systems. Set up checks and alerts to ensure your policy engines and data pipelines are running smoothly [21].
Step 5: Measure KPIs and Conduct Regular Audits
Tracking actions is just the beginning. To ensure your compliance monitoring system delivers results, you need to transform raw data into actionable insights. This means keeping a close eye on key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting regular audits.
Define Key Compliance Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Start by setting clear metrics to evaluate the health of your compliance program. One of the most critical KPIs is control effectiveness, which measures whether your automated controls align with framework requirements [24]. Kaitlyn Archibald, Senior Product Marketing Manager at OneTrust, highlights its importance:
"Control effectiveness is a foundational KPI to gauge and evolve your program over time." [24]
Operational efficiency is another area to monitor. This includes metrics like task completion times and automation coverage - the percentage of tasks successfully handled by automation [4][5]. Pay attention to error rates and how quickly flagged incidents are resolved [4][24][8]. For instance, if you’re running automated lead generation campaigns with tools like Cohesive AI, it’s crucial to track how quickly compliance issues in email campaigns are identified and addressed. Platforms like Cohesive AI make it easier to monitor these KPIs in real time.
Engagement metrics also play a significant role. Keep tabs on policy attestation rates and training completion to ensure your team understands and adheres to compliance requirements [23]. The U.S. Department of Justice stresses the importance of proving that compliance programs are not just in place but actively working. This includes verifying that employees are accessing and engaging with internal policies [23].
For risk management, track the number and nature of violations, reporting rates per 1,000 employees, and trends in retaliation reports [23]. These insights can give you a clearer picture of your organization’s compliance health.
Despite the growing reliance on technology, there’s room for improvement. While 63% of Chief Compliance Officers anticipate increased budgets for automation and AI, only 33% currently use bots for repetitive tasks, and just 23% use predictive modeling for compliance monitoring [22]. The stakes are high - consider the $37,812,859 in SEC enforcements issued during a single 30-day period in late 2025 or the record $1.3 billion penalty FinCEN imposed on TD Bank in 2024 for Bank Secrecy Act violations [1][8].
Once you’ve defined your KPIs, the next step is to validate them through regular audits.
Schedule Routine Compliance Audits
Using these metrics as a foundation, regular audits are essential for ensuring compliance and maintaining system integrity. Instead of scrambling at the end of the year, adopt a continuous compliance approach. Automated 24/7 monitoring is a valuable tool but should complement - not replace - scheduled audits [5][8].
Set a quarterly schedule to review automated logs, test alert thresholds, and evaluate workflow versions [3]. Simulated audits can also be a game-changer, helping you test your readiness and uncover gaps in your data pipeline or evidence collection process [3]. One G2 reviewer shared their experience:
"Moxo cut our audit prep time in half by automating evidence requests and sign-offs. The dashboards gave us full visibility and confidence for audit readiness." [4]
Framework mapping during audits can streamline the process further. For example, organizations certified under ISO 27001:2022 often find nearly 50% overlap with other frameworks like GDPR, NIST CSF, and PCI DSS. This overlap allows you to consolidate evidence collection and minimize duplicate efforts [24].
Conclusion
Following the framework outlined above, compliance monitoring acts as a safeguard, protecting businesses from the financial and reputational damage that can arise from non-compliance. On average, a single compliance issue can cost companies $4 million in revenue [2]. By adopting a structured monitoring approach, organizations not only reduce these risks but also improve operational efficiency.
The five-step framework discussed earlier provides a reliable system that operates continuously. Leveraging automation can save up to 75% of the time spent on compliance management [24], freeing your team to focus on more strategic initiatives rather than tedious manual processes.
With nearly 50 new regulatory rules being finalized in as little as seven days [1] and enforcement actions reaching 1,558 within a single month in late 2025 [1], the need for real-time oversight has never been greater. Automated workflows help mitigate human error - one of the leading causes of security incidents - and ensure policies are applied consistently across your organization [5][8].
For local service businesses utilizing tools like Cohesive AI for automated lead generation, compliance monitoring can seamlessly integrate into email workflows. This ensures regulatory standards are upheld while scaling outreach efforts. Start by focusing on one critical area, measure the outcomes, and then expand your efforts [5].
Key Takeaways
The success of compliance monitoring hinges on three essential components: People (teams with clearly defined roles), Process (established thresholds and actionable playbooks), and Platform (centralized tools for logging and transparency) [3]. When any one of these elements is missing, vulnerabilities are likely to arise.
While automation is invaluable for handling repetitive tasks, human expertise remains critical for interpreting policies and making high-stakes decisions [4][7]. As the Rutgers School of Law emphasizes:
"An organization that has made a robust effort to prevent and detect violations of the law by its employees and others acting for it will be treated less harshly than one that was indifferent to complying with the law." [2]
By implementing structured workflows, businesses can achieve a 30% reduction in compliance incidents within a year, while those with effective tracking systems report a 25% decrease in non-conformities [7]. These improvements not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce the time spent on audits and allow businesses to scale without significantly increasing compliance resources.
Adopting these practices will help secure your operations and maintain confidence in your regulatory compliance efforts.
FAQs
What compliance standards should I follow when automating workflows?
To keep your automated workflows in line with regulations, it's crucial to align with the appropriate legal frameworks based on the data you handle and your business operations. For companies in the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a key consideration, especially when managing personal data. If your business involves data from EU residents, you’ll need to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). For AI-driven processes, the EU AI Act lays out specific requirements for safety and transparency. Additionally, publicly traded companies or those involved in financial reporting must adhere to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) to ensure proper internal controls and audit trails.
To ensure compliance, incorporate these steps into your workflows:
Implement measures to enforce consent and protect personal data under CCPA and GDPR.
Record model inputs, outputs, and any actions taken to reduce bias, as outlined by the EU AI Act.
Keep unalterable audit records to meet SOX requirements.
Tools like Cohesive AI can make this process easier by automating data checks, ensuring policies are followed, and creating audit-ready documentation. This allows you to concentrate on your core business activities without getting overwhelmed by regulatory demands.
How do automation tools improve compliance monitoring in workflows?
Automation tools are reshaping compliance monitoring by replacing manual, time-intensive processes with real-time, data-driven workflows. These tools can instantly track regulatory updates, monitor policy changes, and flag potential risks, ensuring no critical detail slips through the cracks. Tasks are automatically assigned to the appropriate team members, with deadlines clearly tracked to maintain accountability.
By integrating systems like document repositories, CRM platforms, and certification databases, automation provides a centralized, always-current view of compliance requirements. This eliminates repetitive data entry, reduces the chances of human error, and ensures that all obligations are handled promptly.
AI-powered capabilities take compliance a step further by analyzing data to uncover risks, spotting deviations from policies, and generating reports that are ready for audits. This efficient process not only saves time and cuts costs but also allows teams to concentrate on more strategic priorities while maintaining a clear, audit-ready framework.
Why is keeping an audit trail essential for automated workflows?
Maintaining an audit trail is essential because it creates a detailed, traceable record of every step in your automated workflows. This not only promotes transparency but also helps meet regulatory requirements and strengthens trust with important stakeholders, such as customers and board members.
Additionally, having a thorough audit trail ensures your system is ready for audits at any time. It also aids in spotting potential compliance issues early, which can reduce risks and enhance accountability across your operations.